
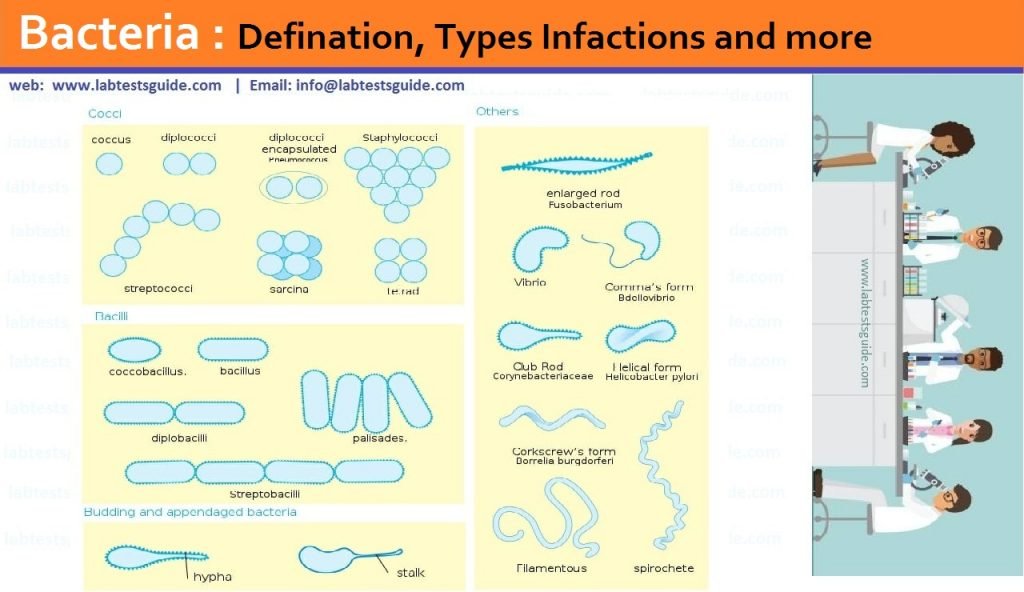
are representatives of gram-positive diplococci. and Moraxella catarrhalis are examples of gram-negative diplococci whereas Streptococcus pneumoniae and Enterococcus spp. They can also be both gram-negative and gram-positive. They are grouped in pairs, implying two coccus cells are linked together. They are given names based on the arrangement of their bacterial cells.Ĭocci bacteria definition states that a diplococcus (plural diplococci) is a coccus (round bacterium) that usually appears as two joined cells. Diplococcus bacteria, Streptococcus bacteria, Staphylococcus bacteria, and the Enterococcus bacteria are all the types of coccus bacteria. Sarcina ventriculi).ĭepending on the type of cocci, as they divide or reproduce, they form distinct patterns. Sarcina is a bacterial genus that consists of eight cocci arranged in a cuboidal pattern (e.g. Tetrads are groups of four cocci that are organized in the same plane (e.g. Staphylococci are colonies of cocci that are irregular (grape-like) (e.g. Those that stay attached may be divided into three categories based on their cellular arrangement:Ĭocci that are in pairs are known as diplococci (examples include, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria gonorrhoeae). The cocci bacteria can be found as single cells or as cells that stay attached after cell division. Nosocomial (hospital-acquired) infections are normal. This could damage about every body tissue, most commonly the skin. A significant human pathogen is Staphylococcus aureus. Most of these organisms generate carotenoids, which give their colonies a yellow or orange colour. Sugars are fermented, and lactic acid is produced as a byproduct.
BACTERIA SHAPES AND ARRANGEMENT EXPLAINED SKIN
Human skin is indeed home to Staphylococcus spp., although they are facultative anaerobes. Physiologically and geographically, the different gram-positive cocci vary. Staphylococcus species do not divide in a normal plane. Diplococci is the scientific name for them. pneumoniae, for particular, has strings that are just two cells long. Since division often happens in the same plane, Streptococcus spp. Sarcina cells, for instance, are organized in cubical pockets since cell division occurs in three perpendicular planes during frequent intervals. The dynamics of cell division as well as the reality that cells remain together are reflected in such arrangements. The manner in which the cells are bound with one another distinguishes members of a certain genera: in bags, loops, or grape-like clusters. They're all approximately spherical, but they're all of the different sizes. Gram-positive cocci are a diverse group of bacteria that share a common morphology. Cocci may be pathogenic (e.g., streptococcus), commensal, or symbiotic when residing in their host organism. Gram-positive (thick peptidoglycan layers) as well as gram-negative (thin peptidoglycan layers) cocci have different cell wall structures (thin peptidoglycan layers). The coccus bacterial shape varies depending on whether the bacterial wall is gram-positive or gram-negative. Numerous cocci bacteria lack flagella and therefore are non-motile, in comparison to so many other bacilli-shaped bacteria.Ĭocci is an English loanword for a traditional or neo-Latin noun that comes from the Greek masculine noun κόκκoς (cóccos), which implies "berry." Based on the orientation and connection throughout cell division, the coccus shape may develop in pairs, lines, or bundles. The genus Coccus refers to the form of bacteria and may include several genera, including staphylococci and streptococci. Bacteria are divided into three groups based on their coccus shape: bacillus (rod-shaped), cocci (spherical shaped bacteria), and spirochetes (spiral-shaped). Any bacteria or archaeon with an ovoid, spherical-shaped bacteria or usually round shaped bacteria is called a coccus (plural cocci).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
